Layer 2 may identify devices by a physical address burned into the network card
Layer 2 identifies the applications that are communicating
Layer 3 represents a hierarchical addressing scheme
Layer 4 directs communication to the proper destination network
Layer 4 addresses are used by intermediary devices to forward data
cisco certification 200-125 ccna exam preparation with practice questions and Answers
Which three factors should be considered when implementing a Layer 2 protocol in a network? (Choose three.)
the Layer 3 protocol selected
the geographic scope of the network
the PDU defined by the transport layer
the physical layer implementation
the number of hosts to be interconnected
What determines the method of media access control? (Choose two.)
network layer addressing
media sharing
application processes
logical topology
intermediary device function
What is a function of the data link layer?
provides the formatting of data
provides end-to-end delivery of data between hosts
provides delivery of data between two applications
provides for the exchange data over a common local media
What is a characteristic of a logical point-to-point topology?
The nodes are physically connected.
The physical arrangement of the nodes is restricted.
The media access control protocol can be very simple.
The data link layer protocol used over the link requires a large frame header.
The physical arrangement of the nodes is restricted.
The media access control protocol can be very simple.
The data link layer protocol used over the link requires a large frame header.
A network administrator has been asked to provide a graphic representation of exactly where the company network wiring and equipment are located in the building. What is this type of drawing?
logical topology
physical topology
cable path
wiring grid
access topology
What are three characteristics of valid Ethernet Layer 2 addresses? (Choose three.)
They are 48 binary bits in length.
They are considered physical addresses.
They are generally represented in hexadecimal format.
They consist of four eight-bit octets of binary numbers.
They are used to determine the data path through the network.
They must be changed when an Ethernet device is added or moved within the network.
They are considered physical addresses.
They are generally represented in hexadecimal format.
They consist of four eight-bit octets of binary numbers.
They are used to determine the data path through the network.
They must be changed when an Ethernet device is added or moved within the network.
What two facts are true when a device is moved from one network or subnet to another? (Choose two.)
The Layer 2 address must be reassigned.
The default gateway address should not be changed.
The device will still operate at the same Layer 2 address.
Applications and services will need additional port numbers assigned.
The Layer 3 address must be reassigned to allow communications to the new network.
The default gateway address should not be changed.
The device will still operate at the same Layer 2 address.
Applications and services will need additional port numbers assigned.
The Layer 3 address must be reassigned to allow communications to the new network.
Which statements describe the logical token-passing topology? (Choose two.)
Network usage is on a first come, first serve basis.
Computers are allowed to transmit data only when they possess a token.
Data from a host is received by all other hosts.
Electronic tokens are passed sequentially to each other.
Token passing networks have problems with high collision rates.
Computers are allowed to transmit data only when they possess a token.
Data from a host is received by all other hosts.
Electronic tokens are passed sequentially to each other.
Token passing networks have problems with high collision rates.
What is the purpose of the preamble in an Ethernet frame?
is used as a pad for data
identifies the source address
identifies the destination address
marks the end of timing information
is used for timing synchronization with alternating patterns of ones and zeros
identifies the source address
identifies the destination address
marks the end of timing information
is used for timing synchronization with alternating patterns of ones and zeros
Refer to the exhibit. A frame is being sent from the PC to the laptop. Which source MAC and IP addresses will be included in the frame as it leaves RouterB? (Choose two.)
Refer to the exhibit. A frame is being sent from the PC to the laptop. Which source MAC and IP addresses will be included in the frame as it leaves RouterB? (Choose two.)
source MAC – PC
source MAC – S0/0 on RouterA
source MAC – Fa0/1 on RouterB
source IP – PC
source IP – S0/0 on RouterA
source IP – Fa0/1 of RouterB
Refer to the exhibit. How many unique CRC calculations will take place as traffic routes from the PC to the laptop?
Refer to the exhibit. How many unique CRC calculations will take place as traffic routes from the PC to the laptop?
What is the primary purpose of the trailer in a data link layer frame?
define the logical topology
provide media access control
support frame error detection
carry routing information for the frame
provide media access control
support frame error detection
carry routing information for the frame
What is true regarding media access control? (Choose three.)
Ethernet utilizes CSMA/CD
defined as placement of data frames on the media
contention-based access is also known as deterministic
802.11 utilizes CSMA/CD
Data Link layer protocols define the rules for access to different media
controlled access contains data collisions
defined as placement of data frames on the media
contention-based access is also known as deterministic
802.11 utilizes CSMA/CD
Data Link layer protocols define the rules for access to different media
controlled access contains data collisions
What is true concerning physical and logical topologies?
The logical topology is always the same as the physical topology.
Physical topologies are concerned with how a network transfers frames.
Physical signal paths are defined by Data Link layer protocols.
Logical topologies consist of virtual connections between nodes.
Physical topologies are concerned with how a network transfers frames.
Physical signal paths are defined by Data Link layer protocols.
Logical topologies consist of virtual connections between nodes.
What is a primary purpose of encapsulating packets into frames?
provide routes across the internetwork
format the data for presentation to the user
facilitate the entry and exit of data on media
identify the services to which transported data is associated
Which options are properties of contention-based media access for a shared media? (Choose three.)
non-deterministic
less overhead
one station transmits at a time
collisions exist
devices must wait their turn
token passing
less overhead
one station transmits at a time
collisions exist
devices must wait their turn
token passing
Which IPv4 subnetted addresses represent valid host addresses? (Choose three.)
172.16.4.127 /26
172.16.4.155 /26
172.16.4.193 /26
172.16.4.95 /27
172.16.4.159 /27
172.16.4.207 /27
172.16.4.155 /26
172.16.4.193 /26
172.16.4.95 /27
172.16.4.159 /27
172.16.4.207 /27
What is the primary reason for development of IPv6?
security
header format simplification
expanded addressing capabilities
addressing simplification
header format simplification
expanded addressing capabilities
addressing simplification
Refer to the exhibit. Host A is connected to the LAN, but it cannot get access to any resources on the Internet. The configuration of the host is shown in the exhibit. What could be the cause of the problem?
The host subnet mask is incorrect.
The default gateway is a network address.
The default gateway is a broadcast address.
The default gateway is on a different subnet from the host.
Which statements are true regarding IP addressing? (Choose two.) NAT translates public addresses to private addresses destined for the Internet.
Only one company is allowed to use a specific private network address space.
Private addresses are blocked from public Internet by router.
Network 172.32.0.0 is part of the private address space.
IP address 127.0.0.1 can be used for a host to direct traffic to itself.
Private addresses are blocked from public Internet by router.
Network 172.32.0.0 is part of the private address space.
IP address 127.0.0.1 can be used for a host to direct traffic to itself.
What is a group of hosts called that have identical bit patterns in the high order bits of their addresses?
an internet
a network
an octet
a radi
a network
an octet
a radi
Which of the following network devices are recommended to be assigned static IP addresses? (Choose three.)
LAN workstations
servers
network printers
routers
remote workstations
laptops
servers
network printers
routers
remote workstations
laptops
Which three IP addresses are private? (Choose three.)
172.168.33.1
10.35.66.70
192.168.99.5
172.18.88.90
192.33.55.89
172.35.16.5
Which process do routers use to determine the subnet network address based upon a given IP address and subnet mask?
binary adding
hexadecimal anding
binary division
binary multiplication
binary ANDing
hexadecimal anding
binary division
binary multiplication
binary ANDing
What three facts are true about the network portion of an IPv4 address? (Choose three.)
identifies an individual device
is identical for all hosts in a broadcast domain
is altered as packet is forwarded
varies in length
is used to forward packets
uses flat addressing
Which of the following are features of IPv6? (Choose three.)
larger address space
faster routing protocols
data types and classes of service
authentication and encryption
improved host naming conventions
same addressing scheme as IPv4
faster routing protocols
data types and classes of service
authentication and encryption
improved host naming conventions
same addressing scheme as IPv4
Given the IP address and subnet mask of 172.16.134.64 255.255.255.224, which of the following would describe this address?
This is a useable host address.
This is a broadcast address.
This is a network address.
This is not a valid address.
Refer to the exhibit. Why would the response shown be displayed after issuing the command ping 127.0.0.1 on a PC?
Refer to the exhibit. Why would the response shown be displayed after issuing the command ping 127.0.0.1 on a PC?
The IP settings are not properly configured on the host.
Internet Protocol is not properly installed on the host.There is a problem at the physical or data link layer.
The default gateway device is not operating.
A router on the path to the destination host has gone down.
A router interface has been assigned an IP address of 172.16.192.166 with a mask of 255.255.255.248. To which subnet does the IP address belong?
172.16.0.0
172.16.192.0
172.16.192.128
172.16.192.160
172.16.192.168
172.16.192.176
172.16.192.0
172.16.192.128
172.16.192.160
172.16.192.168
172.16.192.176
What subnet mask would a network administrator assign to a network address of 172.30.1.0 if it were possible to have up to 254 hosts?
255.255.0.0
255.255.255.0
255.255.254.0
255.255.248.0
255.255.255.0
255.255.254.0
255.255.248.0
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has to develop an IP addressing scheme that uses the 192.168.1.0 /24 address space. The network that contains the serial link has already been addressed out of a separate range. Each network will be allocated the same number of host addresses. Which network mask will be appropriate to address the remaining networks?
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has to develop an IP addressing scheme that uses the 192.168.1.0 /24 address space. The network that contains the serial link has already been addressed out of a separate range. Each network will be allocated the same number of host addresses. Which network mask will be appropriate to address the remaining networks?
What is the network address of the host 172.25.67.99 /23 in binary?
10101100. 00011001.01000011.00000000
10101100. 00011001.01000011.11111111
10101100. 00011001.01000010.00000000
10101100. 00011001.01000010.01100011
10101100. 00010001.01000011. 01100010
10101100. 00011001.00000000.00000000
10101100. 00011001.01000011.11111111
10101100. 00011001.01000010.00000000
10101100. 00011001.01000010.01100011
10101100. 00010001.01000011. 01100010
10101100. 00011001.00000000.00000000
What two things will happen if a router receives an ICMP packet which has a TTL value of 1 and the destination host is several hops away? (Choose two.)
The router will discard the packet.
The router will decrement the TTL value and forward the packet to the next router on the path to the destination host.
The router will send a time exceeded message to the source host.
The router will increment the TTL value and forward the packet to the next router on the path to the destination host.
The router will send an ICMP Redirect Message to the source host.
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator discovers that host A is having trouble with Internet connectivity, but the server farm has full connectivity. In addition, host A has full connectivity to the server farm. What is a possible cause of this problem?
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator discovers that host A is having trouble with Internet connectivity, but the server farm has full connectivity. In addition, host A has full connectivity to the server farm. What is a possible cause of this problem?
The router has an incorrect gateway.
Host A has an overlapping network address.
Host A has an incorrect default gateway configured.
Host A has an incorrect subnet mask.
NAT is required for the host A network.
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator has assigned the internetwork of LBMISS an address range of 192.168.10.0. This address range has been subnetted using a /29 mask. In order to accommodate a new building, the technician has decided to use the fifth subnet for configuring the new network (subnet zero is the first subnet). By company policies, the router interface is always assigned the first usable host address and the workgroup server is given the last usable host address. Which configuration should be entered into the workgroup server’s properties to allow connectivity to the network?
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator has assigned the internetwork of LBMISS an address range of 192.168.10.0. This address range has been subnetted using a /29 mask. In order to accommodate a new building, the technician has decided to use the fifth subnet for configuring the new network (subnet zero is the first subnet). By company policies, the router interface is always assigned the first usable host address and the workgroup server is given the last usable host address. Which configuration should be entered into the workgroup server’s properties to allow connectivity to the network?
ccna exploration 1 chapter 5 exam answers
What is a component of a routing table entry?
- the MAC address of the interface of the router
- the destination Layer 4 port number
- the destination host address
- the next-hop address
Which portion of the network layer address does a router use to forward packets?
- host portion
- broadcast address
- network portion
- gateway address
What statement describes the purpose of a default route?
A host uses a default route to transfer data to another host on the same network segment.
A host uses a default route to forward data to the local switch as the next hop to all destinations.
A host uses a default route to identify the Layer 2 address of an end device on the local network.
A host uses a default route to transfer data to a host outside the local network when no other route to the destination exists.
A host uses a default route to forward data to the local switch as the next hop to all destinations.
A host uses a default route to identify the Layer 2 address of an end device on the local network.
A host uses a default route to transfer data to a host outside the local network when no other route to the destination exists.
What two characteristics are commonly associated with dynamic routing protocols? (Choose two.)
require no device configuration
provide routers with up-to-date routing tables
require less processing power than static routes require
consume bandwidth to exchange route information
prevent manual configuration and maintenance of the routing table
provide routers with up-to-date routing tables
require less processing power than static routes require
consume bandwidth to exchange route information
prevent manual configuration and maintenance of the routing table
Refer to the exhibit. The network in the exhibit is fully operational. What two statements correctly describe the routing for the topology that is shown? (Choose two.)
Refer to the exhibit. The network in the exhibit is fully operational. What two statements correctly describe the routing for the topology that is shown? (Choose two.)
192.168.0.2 is the next-hop address that is used by R3 to route a packet from the 10.0.0.0 network to the 172.16.0.0 network.
10.0.0.1 is the next-hop address that is used by R1 to route a packet from the 192.168.12.0 network to the 10.0.0.0 network.
192.168.0.1 is the next-hop address that is used by R1 to route a packet from the 192.168.12.0 network to the 172.16.0.0 network.
172.16.0.1 is the next-hop address that is used by R3 to route a packet from the 10.0.0.0 to the 172.16.0.0 network.
192.168.0.1 is the next-hop address that is used by R2 to route a packet from the 172.16.0.0 network to the 192.168.12.0 network.
192.168.0.2 is the next-hop address that is used by R2 to route a packet from the 172.16.0.0 network to the 192.168.12.0 network.
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator notices that there are too many broadcasts on the network. What two steps can the network administrator take to resolve this problem? (Choose two.)
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator notices that there are too many broadcasts on the network. What two steps can the network administrator take to resolve this problem? (Choose two.)
Replace S2 with a router.
Place all servers on S1.
Disable TCP/IP broadcasts.
Subnet the 192.168.0.0 /24 network.
Disable all unused interfaces on the switches.
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is troubleshooting a connectivity problem and needs to determine the address that is used to forward network packets out the network. Using the netstat -r command, the administrator would identify which address as the address to which all hosts send packets that are destined for an outside network?
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is troubleshooting a connectivity problem and needs to determine the address that is used to forward network packets out the network. Using the netstat -r command, the administrator would identify which address as the address to which all hosts send packets that are destined for an outside network?
10.10.10.26
127.0.0.1
10.10.10.6
10.10.10.1
224.0.0.0
Which three statements are true about routes and their use? (Choose three.)
If no route to the destination network is found, the packet is returned to the previous router.
If the destination network is directly connected, the router forwards the packet to the destination host.
If multiple network entries exist for the destination network, the most general route is used to forward the packet.
If no route exists for the destination network and a default route is present, the packet is forwarded to the next-hop router.
If the originating host has a default gateway configured, the packet for a remote network can be forwarded using that route.
If a host does not have a route manually configured for the destination network, the host will drop the packet.
If the destination network is directly connected, the router forwards the packet to the destination host.
If multiple network entries exist for the destination network, the most general route is used to forward the packet.
If no route exists for the destination network and a default route is present, the packet is forwarded to the next-hop router.
If the originating host has a default gateway configured, the packet for a remote network can be forwarded using that route.
If a host does not have a route manually configured for the destination network, the host will drop the packet.
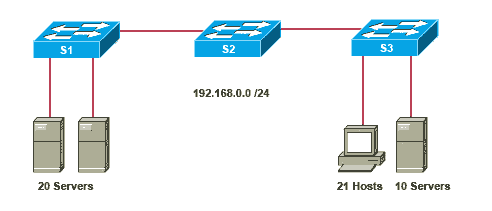
Refer to the exhibit. All devices shown in the exhibit have factory default settings. How many broadcast domains are represented in the topology that is shown?
Refer to the exhibit. All devices shown in the exhibit have factory default settings. How many broadcast domains are represented in the topology that is shown?
3
4
5
7
8
11
What are three common problems with a large network? (Choose three.)
too few broadcasts
performance degradation
security issues
limited management responsibility
host identification
protocol compatibility
performance degradation
security issues
limited management responsibility
host identification
protocol compatibility
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Popular Posts
-
VTY interface console interface Ethernet interface secret EXEC mode privileged EXEC mode router configuration mode
-
source end transfer intermediary
-
The host is unable to communicate on the local network. The host can communicate with other hosts on the local network, but is unable t...
-
The addresses are 48 bits long. Network layer addressing is used by Ethernet switches to make forwarding decisions. It uses a hierarchi...
-
Refer to the exhibit. Host_A is attempting to contact Server_B. Which statements correctly describe the addressing Host_A will generate ...
-
the destination device on the local media the destination host address the bits that will be transferred over the media the source appl...
-
define the structure of layer specific PDU’s dictate how to accomplish layer functions outline the functions necessary for communications...
-
Routers will not allow packets to be forwarded until the network has converged. Hosts are unable to access their gateway until the network...
-
recognizes streams of bits identifies the network layer protocol makes the connection with the upper layers identifies the source and des...