cisco certification 200-125 ccna exam preparation with practice questions and Answers
A network administrator has been told that the company IP address infrastructure must adhere to RFC 1918. What three IP address ranges from RFC 1918 could the administrator use on the network? (Choose three.)
10.0.0.0/8
127.0.0.0/8
169.254.0.0/16
172.16.0.0/12
192.168.0.0/16
209.165.201.0/27
Refer to the exhibit. What can be concluded from the output shown in the exhibit?
Refer to the exhibit. What can be concluded from the output shown in the exhibit?
The routing table is limited to 2 routes.
The LAN interfaces are participating in the routing process.
One update has been sent out of each serial interface and 2 have been received.
The no auto-summary has not been configured on this router.
Refer to the exhibit. What effect will the commands that are shown have on RIP updates for Router1?
Refer to the exhibit. What effect will the commands that are shown have on RIP updates for Router1?
Only version 2 updates are sent to 255.255.255.255.
Only version 2 updates are sent to 224.0.0.9.
Both version 1 and version 2 updates are sent to 224.0.0.9.
Both version 1 and version 2 updates are sent to 255.255.255.255.
Refer to the exhibit. Routers East and West are configured using RIPv1. Both routers are sending updates about their directly connected routes. The East router can ping the West router serial interface and West can ping the serial interface of East. However, neither router has dynamically learned routes from the other. What is most likely the problem?
Refer to the exhibit. Routers East and West are configured using RIPv1. Both routers are sending updates about their directly connected routes. The East router can ping the West router serial interface and West can ping the serial interface of East. However, neither router has dynamically learned routes from the other. What is most likely the problem?
A gateway of last resort is required.
Subnetting is not supported by RIPv1.
VLSM is not supported by RIPv1.
One of the routers needs a clock rate on the serial interface.
What are two reasons to implement RIP version 2 rather than RIP version 1? (Choose two.)
RIP version 2 supports VLSM.
RIP version 2 supports more than 16 routers.
RIP version 2 supports classful (and not classless) routing.
RIP version 2 supports routing update authentication.
RIP version 2 supports multi-areas.
RIP version 2 uses the Dijkstra algorithm rather than the Bellman-Ford algorithm.
A network administrator installed four new routers that are running RIPv2. Router1 is a boundary router in the RIPv2 network and has a default route configured. Once the network has converged, the network administrator enters Router1(config-router)# default-information originate on Router1. How will this affect the network?
prevents Router1 from forwarding updates about networks that are not directly connected
causes all routers in the network to synchronize routing updates with Router1
forces Router1 to become the primary or designated router (DR) for updates
propagates the default route to all routers in the network
is vmware player free ?
 |
| vmware player |
Yes! vmware player is free opposed to VMWare Workstation Which you have to buy. You Can download vmware player at vmware.com
Is VirtualBox Free ?
 |
Yes! VirtualBox is free Open Source Software release under the terms of the GNU General Public License (GPL). You Can download oracle virtualbox at virtualbox.rog.
What field was added to the RIP message header by RFC 1723 to add support for VLSM and CIDR?
subnet mask
destination port number
address family identifier
source and destination IP addresses
How are RIP v1 and RIP v2 similar to one another? (Choose three.)
They both use hop count as a metric.
They both have the same metric value for infinite distance.
They both broadcast their updates to their neighbors.
They both send subnet mask information in their updates.
They both provide for authentication of update sources.
They both use split horizon to prevent routing loops.
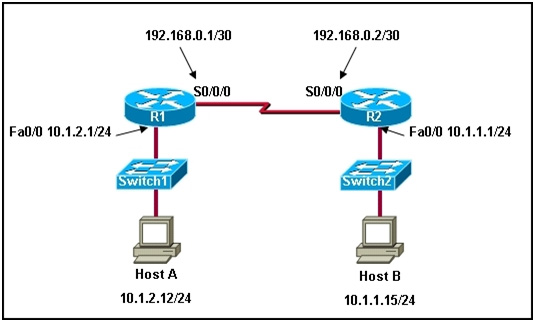
Refer to the exhibit. A network technician enters the static route in R1 needed to reach network 10.1.1.0/24. A ping from R1 to Host B fails. The technician begins testing the network and has the following results:
Refer to the exhibit. A network technician enters the static route in R1 needed to reach network 10.1.1.0/24. A ping from R1 to Host B fails. The technician begins testing the network and has the following results:
1. pings from R1 to the S0/0/0 interface on R2….successful
2. pings from R1 to the Fa0/0 interface on R2….successful
3. pings from Host B to hosts on the 10.1.1.0/24 network….successful
4. pings from Host B to the Fa0/0 interface on R2….successful
5. pings from R2 to Host B….successful
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Popular Posts
-
VTY interface console interface Ethernet interface secret EXEC mode privileged EXEC mode router configuration mode
-
source end transfer intermediary
-
The host is unable to communicate on the local network. The host can communicate with other hosts on the local network, but is unable t...
-
The addresses are 48 bits long. Network layer addressing is used by Ethernet switches to make forwarding decisions. It uses a hierarchi...
-
Refer to the exhibit. Host_A is attempting to contact Server_B. Which statements correctly describe the addressing Host_A will generate ...
-
the destination device on the local media the destination host address the bits that will be transferred over the media the source appl...
-
define the structure of layer specific PDU’s dictate how to accomplish layer functions outline the functions necessary for communications...
-
Routers will not allow packets to be forwarded until the network has converged. Hosts are unable to access their gateway until the network...
-
recognizes streams of bits identifies the network layer protocol makes the connection with the upper layers identifies the source and des...