cisco certification 200-125 ccna exam preparation with practice questions and Answers
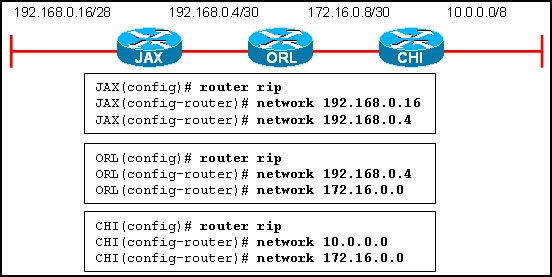
Refer to the exhibit. RIPv1 is running on all three routers. All interfaces have been correctly configured with addresses in the address ranges that are shown. Which route would you see in the routing table on router CHI if the routers are configured with the commands that are displayed in the exhibit?
Refer to the exhibit. RIPv1 is running on all three routers. All interfaces have been correctly configured with addresses in the address ranges that are shown. Which route would you see in the routing table on router CHI if the routers are configured with the commands that are displayed in the exhibit?
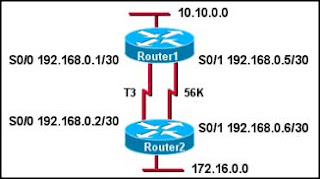
Refer to the exhibit. Router1 is running RIPv1. What command was entered into Router1 to configure the gateway of last resort?
Refer to the exhibit. Router1 is running RIPv1. What command was entered into Router1 to configure the gateway of last resort?
Refer to the exhibit. All routers that are shown are running the RIP routing protocol. All unknown IP traffic must be forwarded to the ISP. What router or set of routers are recommended to have both a default route and the default-information originatecommand issued to implement this forwarding policy?
Refer to the exhibit. All routers that are shown are running the RIP routing protocol. All unknown IP traffic must be forwarded to the ISP. What router or set of routers are recommended to have both a default route and the default-information originatecommand issued to implement this forwarding policy?
Refer to the exhibit. A network consists of multiple routers. What can be verified when the show ip protocols command is issued on one of the routers in the network?
Refer to the exhibit. A network consists of multiple routers. What can be verified when the show ip protocols command is issued on one of the routers in the network?
Refer to the exhibit. All routers in the exhibit are running RIP v1. The network administrator issues the show ip route command on router A. What routes would appear in the routing table output if the network is converged? (Choose two).
Refer to the exhibit. All routers in the exhibit are running RIP v1. The network administrator issues the show ip route command on router A. What routes would appear in the routing table output if the network is converged? (Choose two).
Refer to the exhibit. Router1 and Router2 are running the RIPv1 protocol. The network administrator configures the command network 10.1.0.0 on Router1. What network will Router1 advertise to Router2?
Refer to the exhibit. Router1 and Router2 are running the RIPv1 protocol. The network administrator configures the command network 10.1.0.0 on Router1. What network will Router1 advertise to Router2?
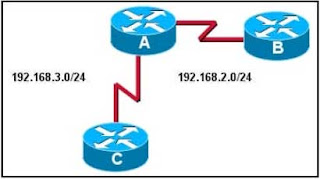
Refer to the exhibit. All routers are configured with valid interface addresses in the indicated networks and are running RIPv1. The network is converged. Which routes are present in the routing tables?
Refer to the exhibit. All routers are configured with valid interface addresses in the indicated networks and are running RIPv1. The network is converged. Which routes are present in the routing tables?
All routers have all routes in their routing table.All routers have all /30 routes, but do not have /24 routes in their routing table.
All routers have all /30 routes. Routers A and E also have some of the /24 routes in their routing table.
Which of the following would be the correct command sequence to enable RIP on Router B for all connected networks?
Which of the following would be the correct command sequence to enable RIP on Router B for all connected networks?
RouterB# router ripRouterB(router)# network 210.36.7.0 RouterB(router)# network 220.17.29.0 RouterB(router)# network 211.168.74.0
What are three characteristics of the RIPv1 routing protocol? (Choose three.)
supports the use of VLSM
uses hop count as a metric
considers a metric of 16 as infinity
has an administrative distance of 110 by default
includes the destination IP address and subnet mask in routing updates
calculates metrics using the Bellman Ford algorithm
Refer to the output from the show ip route command. What can be concluded from the output of this router command?
A preferred route to the destination has not been set.
There are two equal cost paths to network 1.0.0.0.
Both interfaces are being used equally to route traffic.
A variance must be set to load-balance across multiple paths.
Refer to the exhibit. The network that is shown is running RIPv1. The 192.168.10.0/24 network was recently added and will only contain end users. What command or set of commands should be entered on Router1 to prevent RIPv1 updates from being sent to the end user devices on the new network while still allowing this new network to be advertised to other routers?
Refer to the exhibit. The network that is shown is running RIPv1. The 192.168.10.0/24 network was recently added and will only contain end users. What command or set of commands should be entered on Router1 to prevent RIPv1 updates from being sent to the end user devices on the new network while still allowing this new network to be advertised to other routers?
Refer to the exhibit. The Ethernet interface on Router2 goes down and the administrator notices that the route is still in the Router1 routing table. How much longer will Router1 keep the down network in its routing table before marking it as possibly down?
30 seconds
90 seconds
155 seconds
180 seconds
255 seconds
Which of the following is considered a limitation of RIP v1?
RIP v1 does not send subnet mask information in its updates.
RIP v1 is not widely supported by networking hardware vendors.
RIP v1 consumes excessive bandwidth by multicasting routing updates using a Class D address.
RIP v1 requires enhanced router processors and extra RAM to function effectively.
RIP v1 does not support load balancing across equal-cost paths.
RIP v1 authentication is complicated and time-consuming to configure.
What will happen if an interface IP address is entered for the address portion of the network command in a RIPv1 configuration instead of a network address?
The router will reject the command.
A route to the host address will be added to outgoing RIP updates.
A route to the host address will be added to the routing table.
All interfaces in the same classful network as the configured address will be included in the RIPv1 routing process.
Which two statements are true regarding the characteristics of RIPv1? (Choose two).
It is a distance vector routing protocol.
It advertises the address and subnet mask for routes in routing updates.
The data portion of a RIP message is encapsulated into a TCP segment.
The data portion of a RIP message is encapsulated into a UDP segment.
It broadcasts updates every 15 seconds.
It allows a maximum of 15 routers in the routing domain.
Which command or set of commands will stop the RIP routing process?
RouterB(config)# router rip RouterB(config-router)# shutdown
RouterB(config)# router rip RouterB(config-router)# network no 192.168.2.0
RouterB(config)# no router rip
RouterB(config)# router no rip
Which command will display RIP activity as it occurs on a router?
debug ip rip
show ip route
show ip interface
show ip protocols
debug ip rip config
show ip rip database
Which three routing protocols are distance vector routing protocols? (Choose three).
RIPv1
EIGRP
OSPF
IS-IS
RIPv2
Three routers running a distance-vector routing protocol lost all power, including the battery backups. When the routers reload, what will happen?
They will share all routes saved in NVRAM prior to the power loss with their directly connected neighbors.
They will multicast hello packets to all other routers in the network to establish neighbor adjacencie
They will send updates that include only directly connected routes to their directly connected neighbor
They will broadcast their full routing table to all routers in the networ
Refer to the exhibit. What path will packets from the 192.168.1.0/24 network travel to reach the 10.0.0.0/8 network if RIP is the active routing protocol?
Refer to the exhibit. What path will packets from the 192.168.1.0/24 network travel to reach the 10.0.0.0/8 network if RIP is the active routing protocol?
Which two conditions are most likely to cause a routing loop? (Choose two.)
random jitter
implementation of classful addressing
inconsistent routing tables
incorrectly configured static routes
a network converging too quickly
implementation of classful addressing
inconsistent routing tables
incorrectly configured static routes
a network converging too quickly
Which two statements are true regarding the function of the RIPv1 routing updates? (Choose two).
updates are broadcast only when there are changes to the topology
updates are broadcast at regular intervals
broadcast are sent to 0.0.0.0
broadcasts are sent to 255.255.255.255
updates contain the entire network topology
only changes are included in the updates
Which event will cause a triggered update?
an update routing timer expires
a corrupt update message is received
a route is installed in the routing table
the network is converged
The graphic shows a network that is configured to use RIP routing protocol. Router2 detects that the link to Router1 has gone down. It then advertises the network for this link with a hop count metric of 16. Which routing loop prevention mechanism is in effect?
The graphic shows a network that is configured to use RIP routing protocol. Router2 detects that the link to Router1 has gone down. It then advertises the network for this link with a hop count metric of 16. Which routing loop prevention mechanism is in effect?
Refer to the exhibit. The routers in this network are running RIP. Router A has not received an update from Router B in over three minutes. How will Router A respond?
Refer to the exhibit. The routers in this network are running RIP. Router A has not received an update from Router B in over three minutes. How will Router A respond?
Refer to the exhibit. If all routers are using RIP, how many rounds of updates will occur before all routers know all networks?
Refer to the exhibit. If all routers are using RIP, how many rounds of updates will occur before all routers know all networks?
Which two statements describe EIGRP? (Choose two.)
EIGRP can be used with Cisco and non-Cisco routers.
EIGRP sends triggered updates whenever there is a change in topology that influences the routing information.
EIGRP has an infinite metric of 16.
EIGRP sends a partial routing table update, which includes just routes that have been changed.
EIGRP broadcasts its updates to all routers in the network.
What does a router running RIP do first with a new route that is received from an advertisement?
places it immediately in the routing table
adjusts the metric for the new route to show the added distance for the route
advertises this route out all other interfaces except the one that it came in on
sends a ping packet to verify that the path is a feasible route
Which of the following methods does split horizon use to reduce incorrect routing information?
Routing updates are split in half to reduce the update time.
Information learned from one source is not distributed back to that source.
New route information must be learned from multiple sources to be accepted.
The time between updates is split in half to speed convergence.
New route information is suppressed until the system has converged.
Which of the following statements are correct about RIP?
uses a broadcast to update all other routers in the network every 60 seconds
uses a multicast address to update other routers every 90 seconds
will send out an update if there is a failure of a link
updates only contain information about routes that have changed since last update
What is a routing loop?
a packet bouncing back and forth between two loopback interfaces on a route
a condition where a return path from a destination is different from the outbound path forming a “loop”
a condition where a packet is constantly transmitted within a series of routers without ever reaching its intended destination
the distribution of routes from one routing protocol into another
A network administrator is evaluating RIP versus EIGRP for a new network. The network will be sensitive to congestion and must respond quickly to topology changes. What are two good reasons to choose EIGRP instead of RIP in this case? (Choose two.)
EIGRP uses periodic updates.
EIGRP only updates affected neighbors.
EIGRP uses broadcast updates.
EIGRP updates are partial.
EIGRP uses the efficient Bellman-Ford algorithm.
Which of the following can exist in a distance vector network that has not converged? (Choose three).
routing loops
inconsistent traffic forwarding
no traffic forwarding until system converges
inconsistent routing table entries
routing table updates sent to wrong destinations
Which statement is true regarding cisco’s RIP_JITTER variable?
It prevents the synchronization of routing updates by buffering the updates as they leave the router interface
It prevents the synchronization of routing updates by subtracting a random length of time ranging from 0% to 15% of the specified interval time from the next routing update
It prevents the synchronization of routing updates by causing the router to skip every other scheduled update time
It prevents the synchronization of routing updates by forcing the router to listen when its time for other updates on the lines before sending it
What does the RIP holddown timer do?
ensures an invalid route has a metric of 15
prevents a router from sending any updates after it has introduced a routing loop into the network
ensures every new route is valid before sending an update
instructs routers to ignore updates, for a specified time or event, about possible inaccessible routes
prevents a router from sending any updates after it has introduced a routing loop into the network
ensures every new route is valid before sending an update
instructs routers to ignore updates, for a specified time or event, about possible inaccessible routes
What is the purpose of the TTL field in the IP header?
used to mark routes as unreachable in updates sent to other routers
prevents regular update messages from reinstating a route that may have gone bad
prevents a router from advertising a network through the interface from which the update came
limits the time or hops that a packet can traverse through the network before it should be discarded
defines a maximum metric value for each distance vector routing protocol by setting a maximum hop count
prevents regular update messages from reinstating a route that may have gone bad
prevents a router from advertising a network through the interface from which the update came
limits the time or hops that a packet can traverse through the network before it should be discarded
defines a maximum metric value for each distance vector routing protocol by setting a maximum hop count
A router learns two paths with equal metrics to a destination network via the RIP routing protocol. How will the router handle packets to the destination network?
The router will install the first route it learned into the routing table.
The router will install both routes in the routing table and load balance between the two.
The router will put the first route in the routing table, and denote the second route as a backup route.
The router will pick the path with the higher bandwidth and will place it in the routing table.
Refer to the exhibit. If RIP is the routing protocol, what is the value of the metric from router A to network 192.168.5.0/24?
Refer to the exhibit. If RIP is the routing protocol, what is the value of the metric from router A to network 192.168.5.0/24?
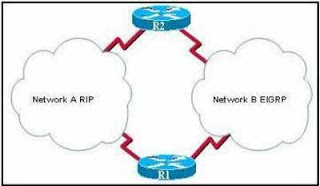
A growing medium-sized manufacturing company recently began to have routing instability issues. The company uses static routes and has a mixture of over 30 Cisco and non-Cisco routers. The network administrator has decided to convert the network to dynamic routing. What characteristics of protocols should be considered in this selection process?
Distance vector routing protocols, such as RIP, converge more quickly than do link-state routing protocols.
EIGRP can be used on all of the routers in the company.
OSPF can be used between the routers.
An exterior routing protocol, such as BGP, is recommended for growing companies.
Refer to the exhibit. Router1 and Router2 are running EIGRP. All interfaces are operational and packets can be forwarded between all networks. What information will be found in the routing table for Router1?
Refer to the exhibit. Router1 and Router2 are running EIGRP. All interfaces are operational and packets can be forwarded between all networks. What information will be found in the routing table for Router1?
When multiple routing protocols have a route to the same destination network, what determines which route is installed in the routing table?
best metric
lowest hop count
greatest available bandwidth
lowest administrative distance
lowest cost
The following line of code is displayed in a routing table: R 209.165.201.0/24 [120/2] via 192.168.252.2, 00:00:16, S0/0/0 What can be concluded from this output?
A packet destined for host 192.168.252.2 will be forwarded out the interface connected to network 209.165.201.0/24.
The value, 120, is used to determine the best path when a router has more than one routing protocol configured for the same destination network.
This route was manually configured using the ip route command.
192.168.252.2 is an interface on the router that produced this output.
Which two statements are true regarding the advantages of the use of static routes? (Choose two).
increased security
reduced effort in configuring routes
the administrator maintains control over routing
easier to implement in a growing network
reduces the chance of routing errors
increased router resource usage
An engineer creates a static route by entering the Router(config)# ip route 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.2 command. What can be concluded about this route?
The administrative distance of this route is 1.
192.168.1.2 is the address of an interface on this router.
This route will display as a directly connected network in the routing table.
Packets with a destination IP address of 192.168.1.2 will be forwarded to the 10.0.0.0/24 network first.
Which of the following conditions must be met in order for a network to have converged?
The routers in the network are operating with dynamic routing protocols.
The routers in the network are operating with compatible versions of IOS.
The routers in the network are operating with the same routing tables.
The routers in the network are operating with consistent routing knowledge.
Why is fast convergence desirable in networks that use dynamic routing protocols?
Routers will not allow packets to be forwarded until the network has converged.
Hosts are unable to access their gateway until the network has converged.
Routers may make incorrect forwarding decisions until the network has converged.
Routers will not allow configuration changes to be made until the network has converged.
Which of the following is associated with link-state routing protocols?
low processor overhead
poison reverse
routing loops
split horizon
shortest-path first calculations
Which of the following best describes the operation of distance vector routing protocols?
They use hop count as their only metric.
They only send out updates when a new network is added.
They send their routing tables to directly connected neighbors.
They flood the entire network with routing updates.
Which two conditions would create a setting where the use of a distance-vector routing protocol would be efficient? (Choose two.)
the network requires a special hierarchical design
fast convergence of the network is crucial
the network is using a hub and spoke topology
the network is using a flat design
there are more than 15 hops between the most distant routers
Which statement is true regarding routing protocols?
RIP uses hop count and bandwidth as the metric for path selection and sendsupdates periodically.
OSPF is a Cisco proprietary protocol that sends updates triggered by topology changes.
EIGRP uses DUAL to calculate the shortest path and can be configured to do unequal cost load balancing.
BGP is a path vector interior routing protocol.
correctly describes how R1 will determine the best path to R2? R1 will install a RIP route using network A in its routing table because the administrative distance of RIP is higher than EIGRP.
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement correctly describes how R1 will determine the best path to R2?
Which command would the network administrator issue to determine if load balancing is in effect on a router?
show ip protocols
show ip route
show ip interface brief
show ip interface
Which two statements correctly describe the concepts of administrative distance and metric? (Choose two.)
Administrative distance refers to the trustworthiness of a particular route.
A router first installs routes with higher administrative distances.
The value of the administrative distance can not be altered by the network administrator.
Routes with the smallest metric to a destination indicate the best path.
The metric is always determined based on hop count.
The metric varies depending which Layer 3 protocol is being routed, such as IP or IPX.
Which two statements are true regarding classless routing protocols? (Choose two.)
sends subnet mask information in routing updates
sends complete routing table update to all neighbors
is supported by RIP version 1
allows for use of both 192.168.1.0/30 and 192.168.1.16/28 subnets in the same topology
reduces the amount of address space available in an organization
What is the purpose of a routing protocol?
It is used to build and maintain ARP tables.
It provides a method for segmenting and reassembling data packets.
It allows an administrator to devise an addressing scheme for the network.
It allows a router to share information about known networks with other routers.
It provides a procedure for encoding and decoding data into bits for packet forwarding.
Which two statements are true regarding metrics? (Choose two.)
RIP uses bandwidth as a metric.
OSPF uses delay as a metric.
EIGRP uses bandwidth as a metric.
OSPF uses cost based on bandwidth as a metric.
RIP uses delay as a metric.
EIGRP uses hop count only as a metric.
What will be the result of the following commands? ORL(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0 ORL(config-if)# ip address 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 ORL(config-if)# no shutdown
The 172.16.3.0 network will be routed by any dynamic routing protocol automatically.
A routing table entry is made to the 172.16.3.0 network with a code of “C”.
A static route is required to route traffic to the 172.16.3.0 network.
The commands will be saved to the startup-configuration.
The following line of code is present in the routing table: O 10.16.1.0/27 [110/129] via 192.168.1.5, 00:00:05, Serial0/0/1 What does the number 129 indicate in this output?
The cost for this link has a value of 129.
The clock rate on this serial interface is set to 129,000.
The next-hop router is 129 hops away from this router.
This route has been updated 129 times in this routing table.
Which two statements describe functions or characteristics of CDP? (Choose two.)
It starts up automatically and allows the device to detect directly connected neighbor devices that use CDP.
It operates at the network layer and allows two systems to learn about each other.
It creates a topology map of the entire network.
It allows systems to learn about each other even if different network layer protocols are configured.
It forwards advertisements about routes for faster convergence.
Which of the following are displayed by the Router# show cdp neighbors command? (Choose three.)
load
platform
reliability
holdtime
local interface
Which piece of information is available from examining the output of the command show ip interface brief?
Interface speed and duplex
Interface MTU
Errors
Interface MAC address
Interface IP address
Refer to the exhibit. Which static route should be configured on Router1 so that host A will be able to reach host B on the 172.16.0.0 network?
Refer to the exhibit. Which static route should be configured on Router1 so that host A will be able to reach host B on the 172.16.0.0 network?
The output of the Router# show interfaces serial 0/1 command displays the following: Serial0/1 is up, line protocol is down. What is the most likely cause for the line protocol being down?
Serial0/1 is shutdown.
There is no cable connecting the routers.
The remote router is using serial 0/0.
No clock rate has been set.
What address can be used to summarize networks 172.16.1.0/24, 172.16.2.0/24, 172.16.3.0/24, and 172.16.4.0/24?
172.16.0.0/21
172.16.1.0/22
172.16.0.0 255.255.255.248
172.16.0.0 255.255.252.0.
172.16.1.0/22
172.16.0.0 255.255.255.248
172.16.0.0 255.255.252.0.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Popular Posts
-
Refer to the exhibit. What two commands will change the next-hop address for the 10.0.0.0/8 network from 172.16.40.2 to 192.168.1.2? (C...
-
VTY interface console interface Ethernet interface secret EXEC mode privileged EXEC mode router configuration mode
-
source end transfer intermediary
-
Refer to the exhibit. Host_A is attempting to contact Server_B. Which statements correctly describe the addressing Host_A will generate ...
-
It connects multiple IP networks. It controls the flow of data via the use of Layer 2 addresses. It determines the best path to send pac...
-
Command : show interfaces status Use In : Privileged EXEC Mode Cisco IOS Command show interfaces status use in switches to view cur...
-
R001 : VMware HA must be functional. R002 : VMware SRM can be used between two sites for DR processes. R003 : You must be able to see all ...
-
service provider edge enterprise WAN applications and devices services module
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has to develop an IP addressing scheme that uses the 192.168.1.0 /24 address space. The n...
-
HA DRS FT Storage DRS